The next-generation computing technology
True integration of memory and computing

Near-Memory Computing
• Concept: Decouples storage and computation but places data closer to computing units.
• Advantages: Reduces data movement latency and power consumption.
• Limitations:
Physical bottlenecks: Performance gains are marginal and costly with current mainstream chip designs.
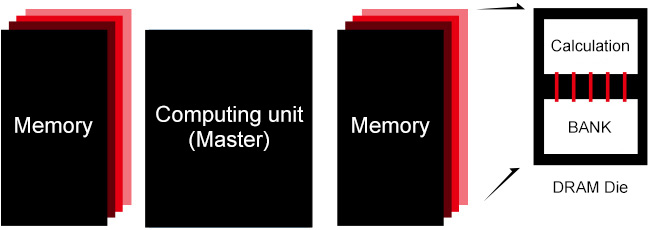
Processing in memory
Tightly Coupled Memory-Compute Integration
• Memory and computing units are co-located at the architectural level
• Utilizes dedicated processing elements embedded within memory arrays
Computing in memory (CIM)
Directly eliminate the boundaries between "storage" and "computing", without the need to move data back and forth.
It significantly enhances the performance of chips, greatly reduces power consumption and keeps costs under control, making it a true integration of memory and computing.
Mature Process Compatibility
- COST 70%
-
Delivers comparable compute power at 70% lower cost
vs von Neumann architectures
- CONSUMPTION 90%
-
Cuts 80–90% power consumption
or equivalent compute tasks
- Process 7 Years
-
Matches traditional architectures' performance
using 7-year-old fabrication tech
- PERFORMANCE 4~10X
-
4–10× faster
in real-world tests(with unoptimized algorithms)
